The KivaKit Manifesto — A New Vision for Java
The KivaKit project is more than a modular application framework for Java.
It’s a new way to think about coding in Java.
The Mission
The mission of KivaKit is to provide a new vision for the development of Java software by providing a design system that takes code reuse to a new level.
The primary goal of the KivaKit coding system is to deeply unify Java coding so that units of reuse (classes and packages) can be discovered and reused blindly, without the need to understand the most common API inconsistencies.
Reuse
Code reuse has improved through various means since the early days of Java. The JDK has improved, providing better APIs as well as modular Java. Third party frameworks like Spring, OSGi, JSF and Apache Wicket, have provided ways to build and reuse code.
But the JDK does not have interfaces consistent enough to discover and use blindly. For example, the java.net
package and the java.io package are both concerned with accessing resources, and they have common integration
points (streams), they do not have the same look and feel to the developer. Network resources and files don’t
have the same semantics. The contents of a package are not accessed in the same way as a folder. Similar
criticisms can be made of aspects of many third-party frameworks.
What we mean by discoverability and blind access here is that many, if not most, aspects of reusable units should not have a learning curve. It should be possible for a developer to discover a new class or package and know how it is structured and how it should behave without learning too much.
Reusable units should have a common structure and consistent behavior that can be relied on.
This sounds like a lofty goal, but how can it work in practice?
KivaKit API Design
KivaKit’s system for designing APIs provides discoverability, common structure, and consistent behavior through:
1. Interface Composition
KivaKit enables the consistent composition of components and packages. Since objects have the same
structure they are easier to recognize. They are also more discoverable because they have the same
recognizable features. KivaKit makes it easy to put objects together in complex ways without abandoning
the familiarity of the Java extends and implements keywords. For example, BaseComponent and
ComponentMixin are defined in terms of many small pieces, each with only a few methods at most:
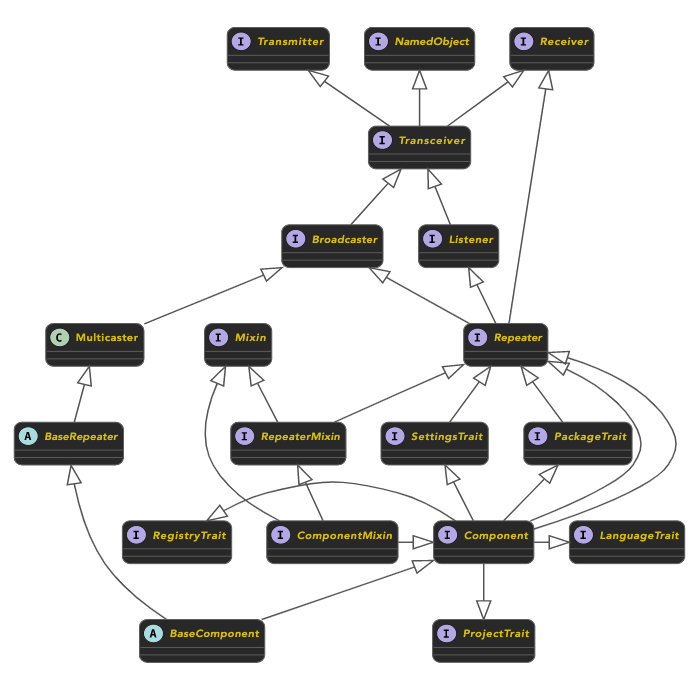
Fine-grained interface composition permits more reuse because code accepting interfaces is applicable to more objects.
Fine-grained interface composition is less fragile because interfaces are smaller and simpler, producing stable contracts that are easy to implement.
2. Mixins
The common structure of reusable units in KivaKit also provides recognizable behavior in the form of inherited and composited features. In KivaKit, objects often provide behavior in two forms. Behavior can be inherited by extending a base class or it can he inherited by implementing an interface:
class Alien extends BaseComponent // Extend abstract class or
class Alien implements ComponentMixin // implement mixin
Here, both forms of inheritance provide Alien with the Component API (see the diagram above),
freeing the developer to build and compose objects without regard to the limitations of Java’s inheritance model.
3. Error Handling
Through messaging behavior (see the diagram above), KivaKit provides consistent and flexible error handling. Errors are handled in the same way, in every component, and by every piece of code. This means we don’t need to make a choice when writing an API. The choice is already made:
- All components in KivaKit obey these error reporting rules:
- Any exceptions caught are converted to broadcast messages
- Any exceptions thrown must be for flow control of fluent method chains
- All code handles errors by listening to messages
This error handling system is flexible enough that we can choose how we want to handle errors for any component at the point of use. Since all KivaKit components report and consume errors in the same way, this relieves an important barrier to both design and consumption of components. We no longer need to know anything about error handling to build or use a component.
4. Application Design
Using consistent error handling and composition, KivaKit provides commonly needed pieces that enable quick and easy application and component design. These components cover common needs, including project structure, applications, components, settings, object discovery, paths, resources, package access, serialization, progress reporting, conversion, validation and so on. KivaKit also unifies key JDK functionality with the KivaKit coding model. This allows most Java code to look and feel the same.
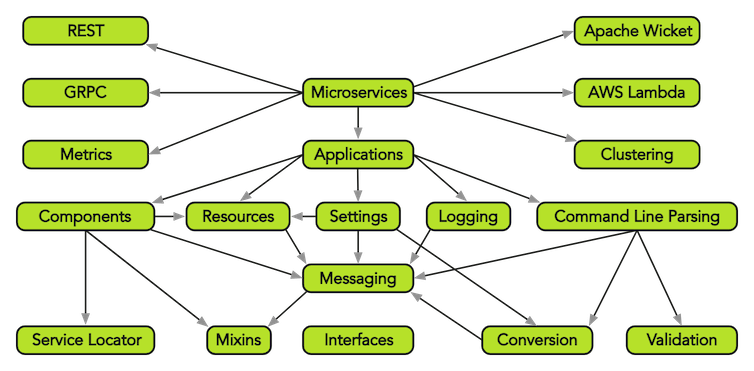
Conclusion
The KivaKit project provides a new way to create objects with common structure and behavior that are easy to discover and use.

